Building smart cities smartly
 Smart cities capitalize on new and existing technologies and insights derived from collected data to transform their way of operation and service deliveries. Engineers work hard – rewiring and reprogramming the city’s infrastructure – to provide the city’s residents with improved quality of life and dynamic economic climate. However, these cities also face monetary, resource, security and legal constraints that frequently change the objectives of the smart city. This means that only with proper collaboration, planning and application can residents actually help identify opportunities and reap benefits from them.
Smart cities capitalize on new and existing technologies and insights derived from collected data to transform their way of operation and service deliveries. Engineers work hard – rewiring and reprogramming the city’s infrastructure – to provide the city’s residents with improved quality of life and dynamic economic climate. However, these cities also face monetary, resource, security and legal constraints that frequently change the objectives of the smart city. This means that only with proper collaboration, planning and application can residents actually help identify opportunities and reap benefits from them.
Experts predicted that urban population would be doubled by 2050, which would mean that the existing cities will need to become smarter to be able to handle this rapid urbanization and all the challenges that come with it. Smart cities are, therefore, built with smart intelligent infrastructure systems, such as smart grids, security solutions, building automation and traffic control systems. All this integrated technological innovation help in improving the economic and environmental conditions of the city. Understanding the benefits of smart cities and its acceptability to the urban population globally, leaders all around the world are desperately trying to build such cities. The latest to join this bandwagon is the Indian subcontinent wherein Mr. Narendra Modi, India’s PM, announced his vision of setting up 100 smart cities across the country.
Technologies used to build smart cities
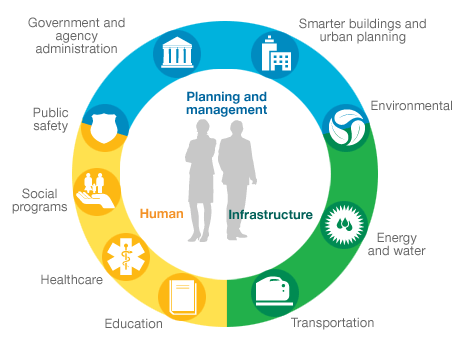
Smart cities use technologies that foster green development, innovation and new citizen participation. Market experts think that innovative concepts that deal with energy and climate change, open government, sustain mobile environment and urban resilience are needed to build a smart city. As Internet users double across the world and the peer-to-peer connectivity strengthens, smart cities become more of a “live” ecosystem wherein connected networks and nodes capture and strengthen real time activities of individuals. The insight and data generated and analyzed here would ultimately enable the citizens of smart cities to thrive optimally.
All smart cities embrace a comprehensive approach in attaining their objectives so that sustainable development is in place and persistent challenges are addressed. To cite an instance, Toronto’s waterfront development embodies this principle to provide flood protection to the area and thereby unlocks significant economic developments.
Integrating technologies like Web 2.0, social media platforms, advanced analytics and access to public data would help in improving services for everyone in a smart city. To cite an instance, use of portable medical devices in the healthcare sector would allow healthcare professionals to access information of patients in real time and enable seamless decision-making. This communication and connectivity between machine and humans would help in leveraging capacities across all infrastructures. The benefits do not end here. Streamlined connectivity is also expected to transform education systems and ability to access information for all stakeholders in the city. Furthermore, collaborative platforms, cloud, and technologies like robotics, AI, 3D printing would also have profound effects on the quality of life of settlers in the smart city.
Are smart cities vulnerable?
Security experts fear that the connectivity existing in smart cities make them vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Market experts on video surveillance equipment argues that existence of wireless sensors that controls everything from healthcare to traffic to the functioning of the government, can actually make a city stop functioning when hacked into, wreaking havoc everywhere.
This is not a hypothetical threat. Extensive research on the technologies used by smart cities have actually discovered hacking groups that targeted power networks across the US and Europe. If the city can be easily hacked into and security problems created everywhere, the smart city would cease to remain “smart” and become a “dumb” one. Therefore, leaders need to start devising and implementing solutions to provide security just as a corporate network might.
Even if smart city is comparatively a new concept for man, it cannot function in isolation. Smart cities can only be successful when all stakeholders collaborate and contribute effectively for creation of an efficient smart city. This means that the recipe for building and sustaining such a city needs to be correct for it to be successful. This can only be done when all the integrated technology in use are secure, and stakeholders of the city are interested in building a sustainable environment. Only then would the smart city grow and give something to everyone. As Canadian journalist Jane Jacobs wrote, “Cities have the capability of providing something for everybody only because and only when they are created by everybody.”